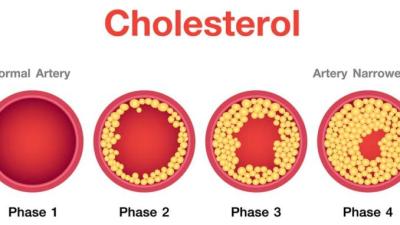
Hyperlipidemia (High Cholesterol)
Hyperlipidemia refers to high levels of lipids (fats) in the blood, including cholesterol and triglycerides. It can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. If diagnosed with hyperlipidemia, work closely with a healthcare provider. They will conduct tests to determine lipid levels and assess overall cardiovascular risk.
Lifestyle Modifications:
-
Healthy Diet: Adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit saturated and trans fats, as well as refined sugars.
-
Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week.
-
Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise.
-
Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, quitting can improve lipid levels and overall heart health.
-
Limit Alcohol: If you drink, do so in moderation. For men, this means up to two drinks per day; for women, one drink per day.
Living With Hyperlipidemia
-
Medication: Depending on your lipid levels and cardiovascular risk, your doctor may prescribe medication. Take medications as directed and attend follow-up appointments to monitor their effectiveness and any potential side effects.
-
Regular Monitoring:
• Lipid Profile: Have regular blood tests to monitor lipid levels. This helps determine if your treatment plan is effective.
• Blood Pressure: Keep track of your blood pressure, as high blood pressure often coexists with hyperlipidemia. -
Compliance: Adhere to the treatment plan recommended by your healthcare provider. This includes taking medications as prescribed and making necessary lifestyle changes.
-
Education: Learn about the importance of hyperlipidemia management, the role of medications, and how lifestyle changes can improve your health.
-
Disease Management:
• Know Your Numbers: Understand your cholesterol levels, including LDL ("bad" cholesterol), HDL ("good" cholesterol), and triglycerides.
• Follow-Up: Attend regular follow-up appointments with your doctor to review your progress and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
-
Emergency Preparedness:
• Recognize Symptoms: Be aware of signs of heart attack or stroke, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, sudden weakness, or slurred speech.
• Emergency Action: If you experience any symptoms of heart attack or stroke, call emergency services immediately.
• Communication: Maintain open communication with your healthcare provider. Discuss any concerns, questions, or changes in your health.
Hyperlipidemia management is a lifelong commitment. With proper medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring, you can reduce your risk of heart disease and enjoy better overall health.
Remember, this guide is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment or any other medical concern.
In an emergency, please call 911 immediately!
